As industries continue to evolve, the use of replacement materials has become a crucial aspect of manufacturing and construction. In this guide, we will delve into the world of replacement materials, exploring their significance, types, factors to consider, and recent innovations.
Get ready to uncover the key insights that shape the future of material science.
Introduction to Replacement Materials
Replacement materials refer to alternative substances or components used in manufacturing or construction processes when the original materials are not available, too costly, or environmentally unsuitable. These materials are essential in ensuring the continuity of production and the completion of projects.
Using replacement materials is crucial for maintaining efficiency, reducing costs, and meeting sustainability goals. By substituting original materials with suitable alternatives, industries can adapt to changing market conditions, reduce waste, and minimize the environmental impact of their operations.
Examples of Industries Using Replacement Materials
- The automotive industry often utilizes recycled plastics and composite materials as replacements for traditional metal parts, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
- In the construction sector, engineered wood products like plywood and oriented strand board are commonly used as substitutes for solid timber, offering cost savings and enhanced structural performance.
- The electronics industry relies on tin-based solders as replacements for lead-based ones to comply with environmental regulations and ensure product safety.
Types of Replacement Materials
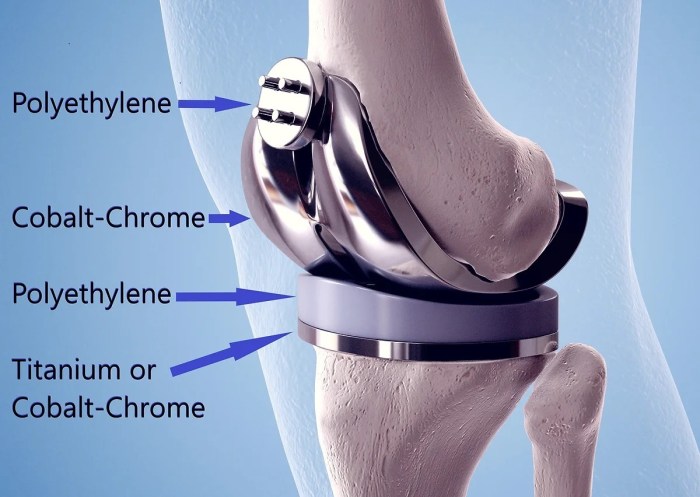
When it comes to replacement materials, there are several types that are commonly used in various industries. Each type has its own unique properties and applications, along with advantages and disadvantages that should be considered.
Composites
Composites are materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties. These materials are combined to create a stronger, more durable material that can be tailored to specific applications. Examples of composites include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and reinforced concrete.Applications:
Aerospace industry
Composite materials are used in the manufacturing of aircraft components such as wings, fuselage, and interior panels.
Automotive industry
Composites are used in the production of car bodies, bumpers, and interior parts for their lightweight and high strength properties.Advantages:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Corrosion resistance
- Design flexibility
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to traditional materials
- Limited repairability in some cases
Polymers
Polymers are materials made up of long chains of molecules that can be synthetic or natural. They are known for their lightweight properties, flexibility, and ease of processing. Examples of polymers include plastics, rubber, and silicone.Applications:
Packaging industry
Polymers are widely used in packaging materials such as bottles, containers, and films.
Medical industry
Polymers are used in medical devices, implants, and drug delivery systems due to their biocompatibility.Advantages:
- Lightweight
- Low cost
- Chemical resistance
Disadvantages:
- Low heat resistance
- Susceptible to wear and tear over time
Alloys
Alloys are materials made by combining two or more metallic elements to enhance specific properties such as strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance. Examples of alloys include stainless steel, brass, and bronze.Applications:
Construction industry
Alloys are used in building structures, pipelines, and bridges for their strength and durability.
Electronics industry
Alloys are used in the production of electrical wiring, connectors, and circuit boards.Advantages:
- Improved mechanical properties
- Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Customizable properties based on alloy composition
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to pure metals
- More complex manufacturing processes required
Factors to Consider When Choosing Replacement Materials

When selecting replacement materials, several key factors need to be taken into consideration to ensure the success and longevity of the replacement. Factors such as strength, durability, cost, and environmental impact play a crucial role in determining the most suitable replacement materials for a given application.
Strength
Strength is a critical factor when choosing replacement materials, especially in applications where the material will be subjected to heavy loads or stress. The replacement material must have sufficient strength to withstand these forces without experiencing failure or deformation.
Durability
Durability is another important consideration when selecting replacement materials. The material must be able to withstand wear and tear over an extended period of time without deteriorating or losing its structural integrity. Factors such as corrosion resistance, impact resistance, and fatigue resistance contribute to the overall durability of the replacement material.
Cost
Cost is a significant factor that influences the choice of replacement materials. While it is essential to select a material that meets the necessary strength and durability requirements, it is also important to consider the overall cost of the material, including procurement, installation, and maintenance expenses.
Finding a balance between performance and cost is crucial in selecting the most cost-effective replacement material.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental impact is becoming an increasingly important factor in the selection of replacement materials. Choosing materials that are sustainable, recyclable, or environmentally friendly can help reduce the overall carbon footprint of a project. Additionally, considering factors such as energy efficiency, emissions, and waste generation can contribute to a more environmentally conscious approach to material selection.
Innovations in Replacement Materials
With the constant evolution of technology and science, innovations in replacement materials have been at the forefront of transforming traditional manufacturing processes. These advancements not only improve the quality and performance of products but also contribute to sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Advanced Composites
Advanced composites are one of the most significant innovations in replacement materials. These materials are made by combining two or more materials with different properties to create a new material that offers superior strength, durability, and lightweight properties. They are increasingly being used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.
3D Printing Materials
3D printing materials have revolutionized manufacturing processes by enabling the production of complex and customized parts with ease. These innovative materials range from plastics to metals and ceramics, offering a wide range of possibilities for various applications. The ability to print parts on-demand has significantly reduced lead times and waste in production.
Bio-based Materials
With a growing focus on sustainability, bio-based materials derived from renewable sources such as plants, algae, and fungi are gaining popularity as replacement materials. These materials offer biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and often comparable performance to traditional materials. They are being used in packaging, textiles, and construction industries.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, replacement materials play a vital role in modern industries, offering innovative solutions and paving the way for future advancements. By understanding their types, factors to consider, and ongoing innovations, we can better appreciate the dynamic nature of materials used in manufacturing and construction.
Stay informed and stay ahead in the world of replacement materials.
FAQs
What are the key factors to consider when choosing replacement materials?
Key factors include strength, durability, cost, and environmental impact.
What are some examples of industries where replacement materials are commonly used?
Automotive, aerospace, and construction industries frequently utilize replacement materials.
How do innovative materials impact traditional manufacturing processes?
Innovative materials are revolutionizing traditional manufacturing by offering improved efficiency and performance.